This pcap file (click to download) has been collected from a Wireless network in which the User is complaining of significantly slower performance and throughput. You are tasked with identifying the issue. Only one answer is correct.
Possible Answers:
A. The Client Device is executing a Trace Route command
B. The Access Point is Operating in Point Coordinated Function (PCF)
C. The Access Point is operating in Repeater Mode
D. The Client device has an incorrectly configured Subnet Mask
E. The Client device has an incorrectly configured Default Gateway

Close any open windows and then open the "2019 - Hero's Challenge - How is this Happening (Phill Shade)" pcap file. You should see four packets in the packet window.
- Identify the MAC and IP address of the Sender of packet 1. From the Packets view, right click and select View Options. Turn on the columns: Source IP, Source MAC, Destination IP, and Destination MAC, then complete the entries below:
Source MAC = Aironet:31:79:42
Source IP = 192.216.124.189 - This network has a router with the MAC address of 00:30:94:BE:70:68 (Cisco:BE:70:68) on the Ethernet Network. Identify the MAC and IP address of the Destination of packet 1.
Destination MAC = Cisco:BE:70:68
Destination IP = 192.216.124.195 - The sender of packet 1 (the PING-ing device) has the IP address of 192.216.124.189. It is using a subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 and is communicating with 192.216.124.195. Given this information, does the sender believe the destination is on the same or a different subnet?
Answer: Different Subnet - When a station believes the destination IP address is on a different subnet, how does a default gateway (router) come in to play?
Answer: When the target device is on a different subnet, the packet is forwarded to the default gateway to properly route it to the destination subnet - Cisco:BE:70:68 is the Ethernet MAC address of the default gateway router being used by 192.216.124.189. This router is on the wired Ethernet. How does the PING packet get from the wireless originator to the router on the wired Ethernet?
Answer: The ICMP Ping Request is sent to the Clients Access Point for transmission to the wired Distribution System or DS (Ethernet) - Given that the PING packet has been addressed to the MAC address of the router instead of to the true destination, what should the router do with the PING packet?
Answer: The Router should readdress the packet and forward it to the correct destination - 192.216.124.195 is on the same wired network as the router. Why do we not see a copy of the forwarded packet (the PING)?
Answer: The packet has entered the DS (Ethernet) network and the pcap is captured on the WLAN - Evaluate packet 2. What protocol is in use? Who is sending the packet? And what information is being requested?
• Double click on packet 2 and look in the detail
Answer: ARP Request being sent by ArrisGro:53:8a:cd to request the MAC Address of the device with the IP Address of 192.216.124.189 - Packet 3 is the reply to packet 2. What is the MAC address associated with IP address 192.216.124.189?
Answer: Aironet:31:79:42 - Evaluate packet 4 and answer the question "Where did the packet come from; and where did it go at the data link layer (MAC) and at the network layer (IP)?"
Answer:
Source MAC Address: ArrisGro:53:8a:cd with IP Address of 192.216.124.195
Destination MAC Address: Aironet:31:79:42 with IP Address of 192.216.124.189 - Packet 4 does not appear to have been forwarded by the router. How can you confirm this?
Answer: Examine the IP TTL Field - Using your understanding of the relationship between the Data Link Layer and the Network Layer, draw a picture of the stations involved in this conversation and the flow of the packets between these stations.
Answer: The Network Diagram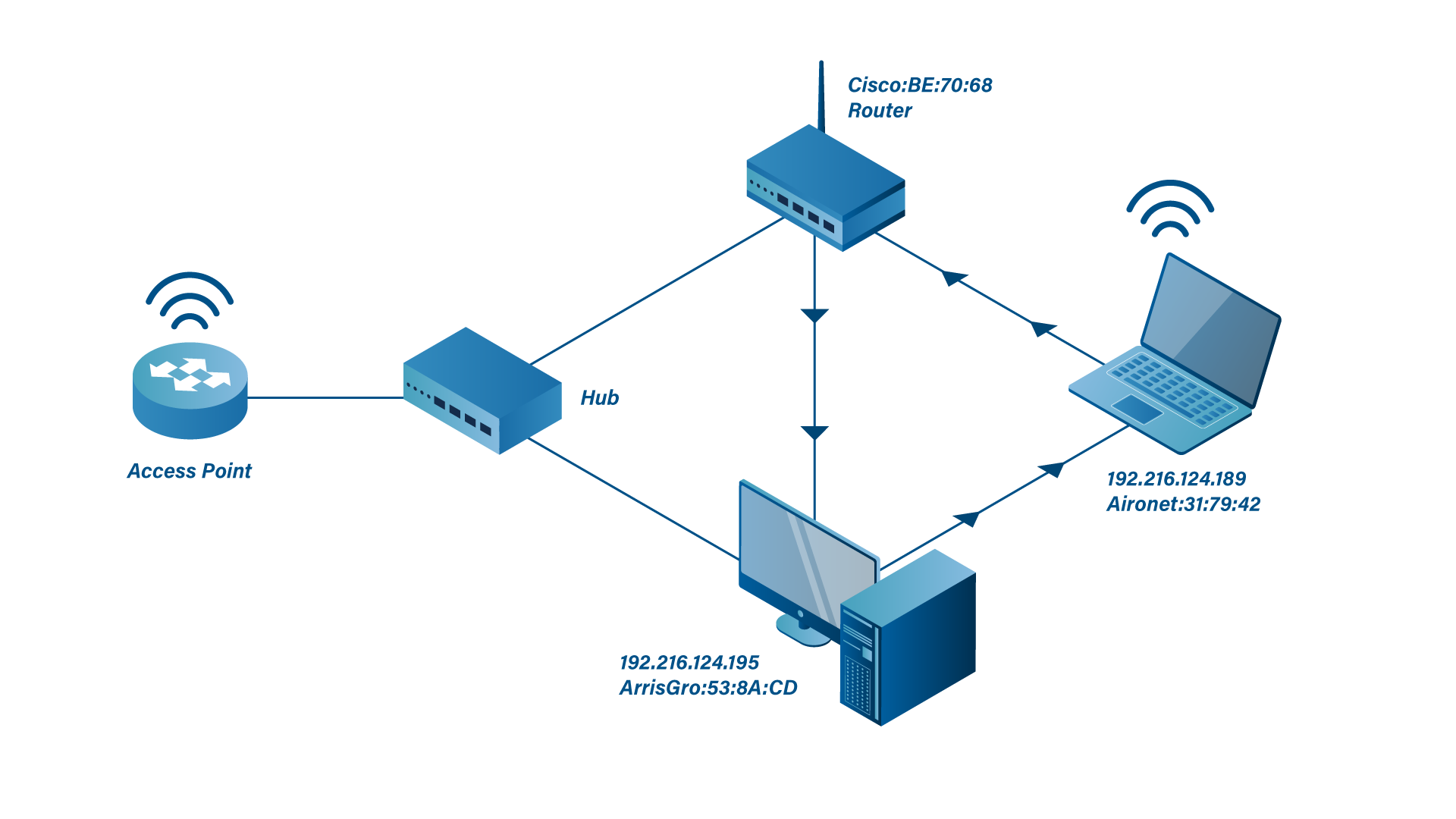
- Based upon your results, what is the issue in the source device?
Answer: Misconfigured subnet mask - What is a possible complaint that a user might have who is experiencing this type of misconfiguration? Explain your answer.
Answer: Slow performance and significantly reduced throughput
Don't forget to check our Wireshark Filters article if you want to learn more about how you can quickly filter all data on Wireshark.
The question was asked by Packet Analysis Hero Phill Shade - Innovative IT and Security Professional.

